Introduction: A Nation Turning Toward a Greener Future
Pakistan’s journey toward renewable energy has evolved from an aspiration to a national necessity. With the ongoing climate challenges, growing power demands, and reliance on imported fuels, the Pakistan Renewable Energy Vision 2025 stands as a roadmap for transformation. This vision not only aims to reduce carbon emissions but also to create a sustainable ecosystem powered by solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass.

⚡ 1. Understanding Pakistan’s Renewable Energy Vision 2025
Launched under the Ministry of Energy (Power Division), Pakistan’s Renewable Energy Vision 2025 outlines clear objectives to shift from fossil fuels toward clean, affordable, and indigenous energy resources. The goal is to achieve 30% renewable energy share by 2030, aligning with global sustainability commitments like the Paris Agreement.

🌞 2. Solar Energy: The Centerpiece of Clean Transformation
Solar energy forms the heart of Pakistan’s renewable agenda. The country’s vast sunlight potential—averaging 5.3 kWh/m²/day—makes it one of the most solar-rich nations globally. Projects like the Quaid-e-Azam Solar Park in Bahawalpur have already showcased the potential of large-scale solar adoption. By 2025, Pakistan aims to install thousands of megawatts in distributed rooftop solar and grid-connected plants.
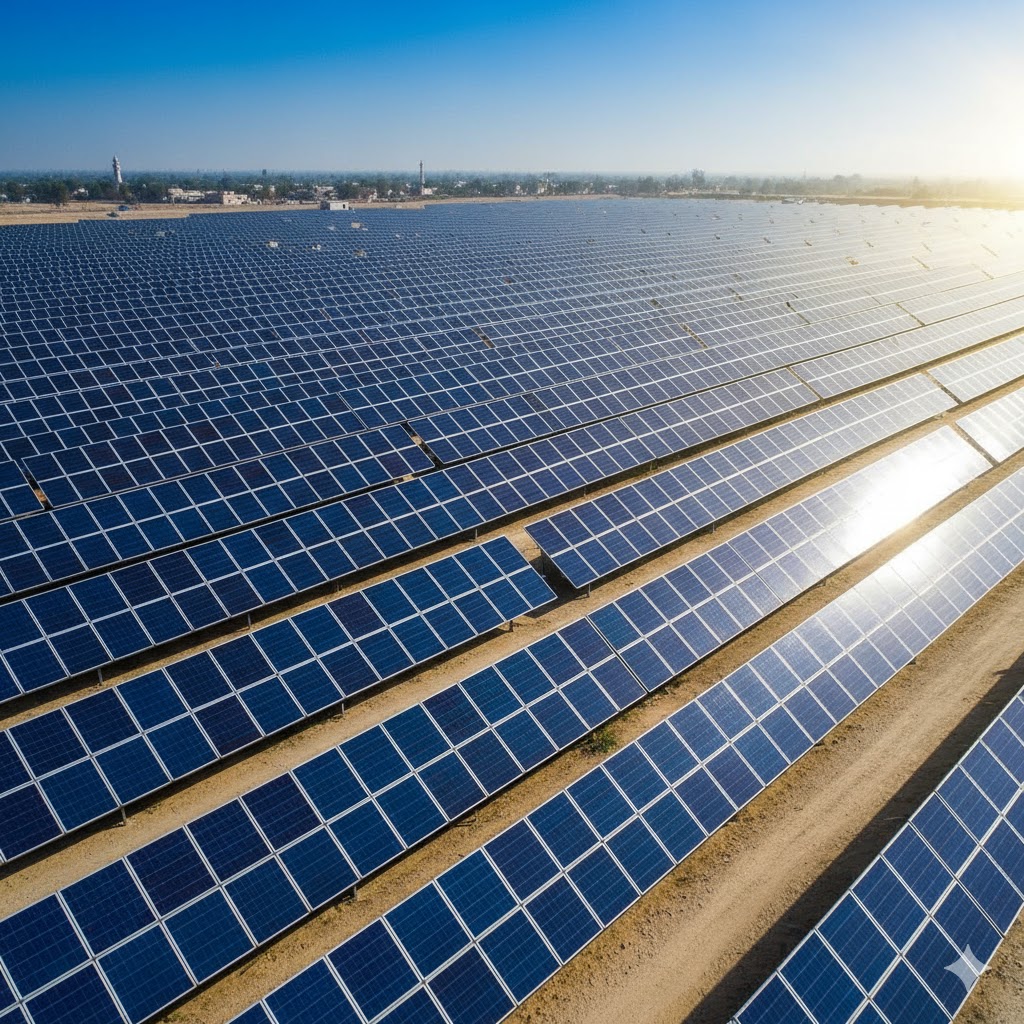

🌬️ 3. Harnessing the Power of Wind Corridors
Wind energy is another vital contributor to the Pakistan Renewable Energy Vision 2025. The Gharo–Jhimpir Wind Corridor in Sindh has become a powerhouse for clean electricity, generating hundreds of megawatts of wind-based energy annually. This zone alone can supply over 50,000 MW if fully developed — reducing dependency on imported fuels.

💧 4. Hydropower: The Backbone of Renewable Mix
Hydropower remains one of Pakistan’s oldest and most reliable renewable sources. Major projects like Diamer-Bhasha, Dasu, and Neelum–Jhelum play a crucial role in meeting long-term power requirements. The government aims to modernize existing dams while integrating small-scale hydropower projects across remote areas by 2025.

🔋 5. Energy Storage and Smart Grid Systems
To complement renewable adoption, Pakistan’s energy plan emphasizes the modernization of grid infrastructure. Smart meters, digital load management, and battery storage systems are being deployed to balance fluctuating supply from renewables. This digital transformation ensures stable electricity and minimizes transmission losses.

🌱 6. Green Financing and Investment Opportunities
Renewable energy growth depends heavily on financing. Under Vision 2025, Pakistan is promoting Green Bonds, international partnerships, and private sector incentives. Institutions like the State Bank of Pakistan are offering low-interest financing for solar and wind projects. These measures attract global investors and stimulate economic growth while reducing emissions.

🌾 7. Biomass and Waste-to-Energy Initiatives
Biomass and waste-to-energy are crucial for circular economy models. Pakistan’s agriculture sector generates millions of tons of crop residue annually—an untapped energy resource. The Vision 2025 framework promotes using agricultural waste, sugarcane bagasse, and municipal waste to generate clean energy for industries and rural communities.

🌏 8. Policy Framework and Institutional Support
The success of Pakistan Renewable Energy Vision 2025 depends on robust policy execution. The Alternative Energy Development Board (AEDB) and National Electric Power Regulatory Authority (NEPRA) are the leading authorities driving implementation. Their regulatory frameworks ensure transparent licensing, competitive tariffs, and investor-friendly conditions.

🏘️ 9. Impact on Households and Small Businesses
For ordinary citizens, Vision 2025 brings tangible benefits — from reduced electricity bills to improved reliability during peak summer months. Solar net metering allows homeowners to feed excess electricity back into the grid, while small businesses can adopt hybrid solar systems for operational savings.
🔮 10. Future Outlook: Toward Net-Zero Pakistan by 2050
The ultimate goal beyond Vision 2025 is achieving Net-Zero Emissions by 2050. This long-term plan integrates renewable energy expansion with electric mobility, efficient urban planning, and sustainable agriculture. Pakistan’s clean energy roadmap reflects a commitment to global climate leadership and self-sufficiency.

📊 Pakistan’s Renewable Energy Achievements So Far
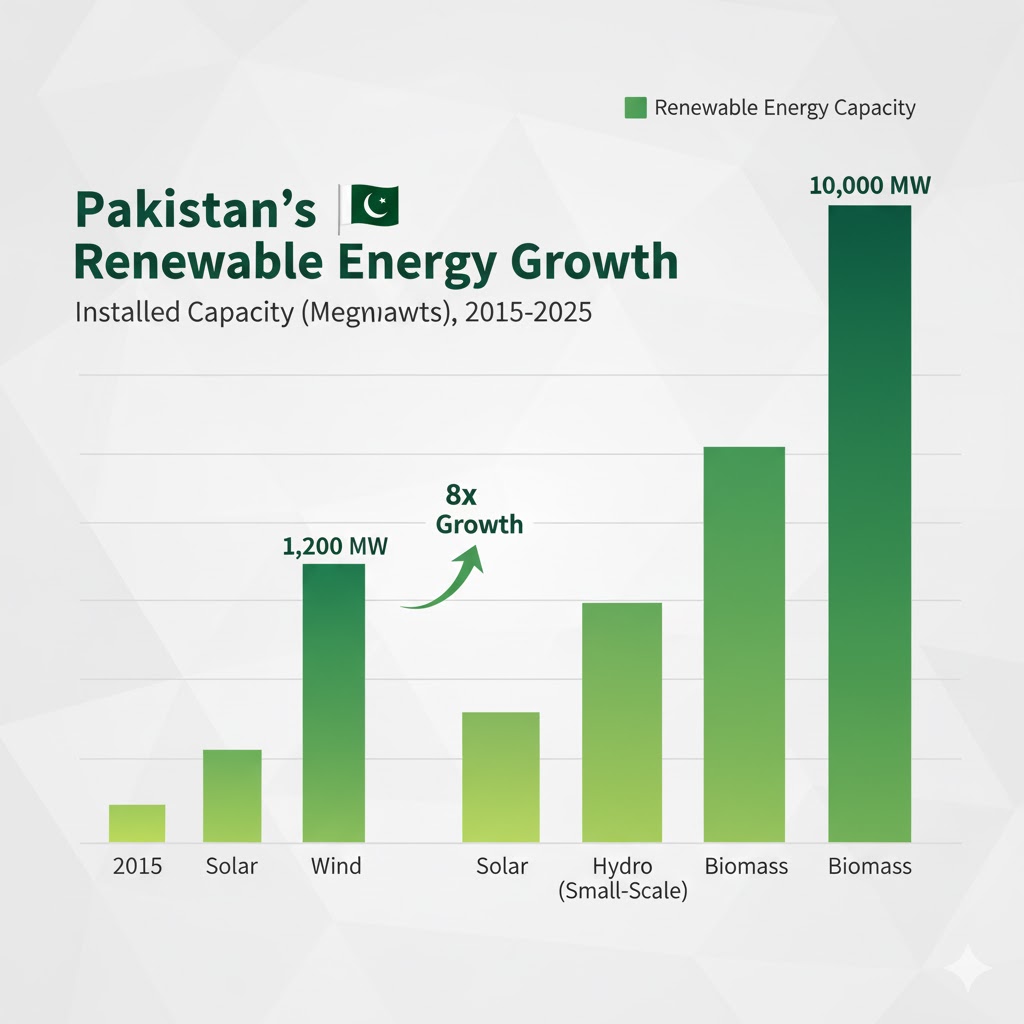
- Over 2,000 MW of wind energy installed.
- Solar projects exceeding 1,500 MW nationwide.
- Hydropower share remains above 25% of total generation.
- Over 50,000 households connected via off-grid renewable systems.
💡 Economic and Environmental Benefits
By implementing its renewable energy goals, Pakistan expects to save billions in fossil fuel imports, create thousands of green jobs, and reduce CO₂ emissions significantly. Clean power also strengthens energy independence, making the national grid more resilient to global fuel price shocks.
🏛️ Government & Global Collaborations
International organizations such as the World Bank, Asian Development Bank (ADB), and UNDP are closely partnering with Pakistan to implement renewable initiatives. Joint ventures and technology transfers are accelerating solar manufacturing, hybrid microgrids, and off-grid electrification projects in rural areas.

FAQ Section: Pakistan Renewable Energy Vision 2025
Q1: What is Pakistan’s Renewable Energy Vision 2025?
It’s a national policy framework aimed at achieving 30% renewable energy in the power mix by 2030 through solar, wind, hydropower, and biomass projects.
Q2: What is the main goal of Vision 2025?
The primary goal is to reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, promote sustainability, and ensure affordable, reliable energy access nationwide.
Q3: How much solar energy potential does Pakistan have?
Pakistan receives one of the highest solar irradiance levels globally—over 5.3 kWh/m²/day—ideal for residential and commercial solar use.
Q4: Which regions are best for wind energy?
Sindh’s Gharo–Jhimpir Corridor is considered the most productive area, followed by coastal regions in Balochistan.
Q5: What role does NEPRA play?
NEPRA regulates the energy sector, issues renewable generation licenses, and ensures transparent tariff mechanisms.
Q6: Are there incentives for domestic solar users?
Yes, solar net metering, tax exemptions on solar equipment, and low-interest green loans are available.
Q7: How will rural areas benefit?
Off-grid solar and mini-hydropower solutions are bringing electricity to remote villages, improving healthcare, education, and livelihoods.
Q8: Is hydropower still relevant in 2025?
Absolutely — hydropower remains crucial, offering steady base-load electricity and supporting grid stability.
Q9: What are the challenges of renewable adoption?
Challenges include policy delays, financing gaps, transmission limitations, and lack of local manufacturing capacity.
Q10: How does Vision 2025 link to Net-Zero 2050?
Vision 2025 sets the groundwork for net-zero emissions by increasing renewable capacity, promoting electric mobility, and improving efficiency.
Q11: Can industries benefit from this transition?
Yes, industries adopting renewables cut costs, earn carbon credits, and align with international environmental standards.
Q12: Is foreign investment growing in Pakistan’s clean energy sector?
Yes, global investors from China, Germany, and the UAE are funding large-scale solar and wind projects under CPEC and green partnerships.
Q13: What are Pakistan’s long-term renewable energy goals?
Beyond 2025, Pakistan aims to achieve 60% clean energy by 2040 and become fully carbon-neutral by 2050.
Q14: How can individuals contribute?
Homeowners can install solar panels, use energy-efficient appliances, and support eco-conscious government initiatives.

Expert Guide: A Green Path Forward
Pakistan’s Renewable Energy Vision 2025 is more than a policy — it’s a promise to future generations. By focusing on innovation, sustainability, and inclusivity, Pakistan can redefine its energy landscape and emerge as a leader in clean technology across South Asia. The journey is challenging, but with public participation and government commitment, a greener Pakistan is within reach.

References:
Visit: NEPRA
Visit: Energy Update
Read More: Pakistan Solar Buy-Back Rate 2025 – Smart Energy Reform















